By Upmanyu Trivedi and Rahul Satija
A bad bank in India that’s expected to launch this month may help reduce one of the world’s worst bad-loan piles but
market participants say it’s a long path ahead.
The new institution, which is set to start operations by the end of June, is likely to handle stressed debt worth 2 trillion rupees ($27 billion) over time, according to a BloombergQuint report. That would be about a quarter of the nation’s non-performing debt load. By housing bad loans of many lenders under one roof, the entity should help speed up decision-making and improve bargaining power when resolving these assets.
But for India to overcome its struggles with bad debt and stabilize the financial system of Asia’s third-largest economy, more fundamental problems with insolvency laws introduced in 2016 need to be addressed, investors say. Their confidence in the country’s bankruptcy reforms has been shaken as creditors’ recovery rates fall, delays in closing cases increase, and liquidations exceed resolutions in the insolvency courts.
Market participants will be watching whether the bad bank focuses on actually resolving the assets rather than keeping them like a warehouse, and whether its team includes appropriate industry and turnaround experts.
“The proposed bad bank is useful as a one-time clean-up exercise of the bad loans that are pending resolution for years now,” said Raj Kumar Bansal, managing director at Edelweiss Asset Reconstruction Co. “But it’s not a long-term solution in dealing with the stressed assets,” he said, adding that bankruptcy reform is key.
Less than one in 10 companies admitted in the insolvency courts is getting resolved while a third are facing liquidation, data compiled by Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India show. The recoveries for financiers from the resolved cases have also dropped to 39% of dues as of March from 46% a year earlier. And if the top nine cases by recovery are excluded, lenders received just 24% of dues, according to Macquarie Capital.
“India’s bankruptcy reforms started off well but they have slowed currently,” said Nikhil Shah, managing director at Alvarez & Marsal India. “Prolonged delays in resolutions, lengthy court battles, and uncertainty of recoveries post-approval of resolution plans are pushing many potential investors away” from the bankruptcy process, he said.
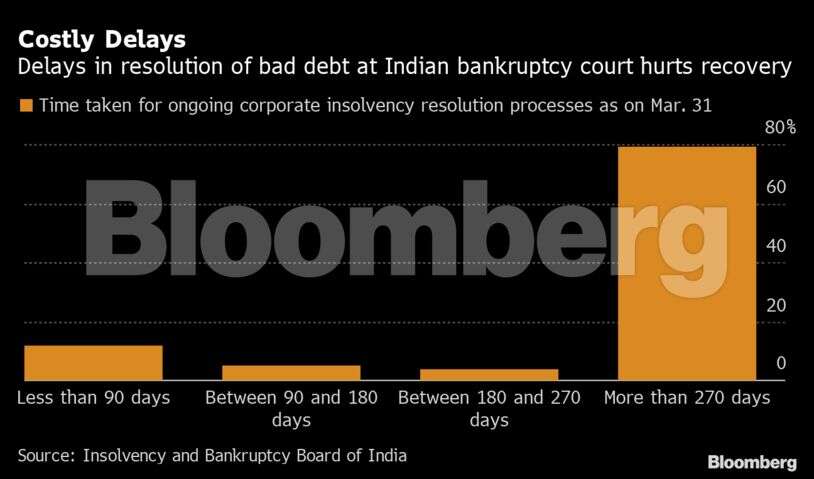
Shah expects the delays in resolutions to worsen further unless the government and judiciary address some of the primary issues, by for example increasing the number of judges and investing in digital infrastructure to boost productivity.
Indian Banks’ Association, which is helping with plans for the proposed bad bank, and Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India, didn’t immediately respond to emails seeking comment.
For now, Indian banks will be happy to finally kick away some of the stressed loans to the proposed entity. The sector’s bad-loan ratio is is set to almost double to 13.5% of total advances by the end of September, India’s central bank said in a report published before the second wave of coronavirus infections hit the country.
“Stressed loans have taken far too much management time across the industry in the past couple of years,” Prashant Kumar, chief executive officer at Yes Bank Ltd., told Bloomberg. “This bad bank will help shift focus from resolving soured loans to improving credit growth.”
