Overseas assets of defaulters, guarantors may soon be within lenders’ reach, BFSI News, ET BFSI
[ad_1]
Read More/Less
Lenders may soon be able to lay their hands on overseas assets of defaulting firms and personal guarantors.
The government has proposed adopting a global model law that will enable lenders to apply the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code to defaulters’ assets lying overseas. These will include the offshore personal assets of the promoter if they have issued a personal guarantee. The changes would also allow the execution of orders against defaulters by overseas courts that have adopted the model law.
The model law is provided by the UNCITRAL — a subsidiary body of the United Nations.
The government has invited public comments on the proposed modifications by December 15.
The model law lays down the basic framework for cooperation between domestic and foreign courts and domestic and foreign insolvency professionals.
Personal guarantors
In the case of a personal guarantor, their ‘habitual’ place of residence will be taken into account to decide the jurisdiction where the main bankruptcy proceedings will happen. Debt recovery tribunals and the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) benches and their appellate tribunals are platforms where overseas creditors could initiate or participate in proceedings against personal guarantors in India.
The introduction of a cross-border insolvency law in the IBC, that is in line with international best practices and suitable for the Indian context, may be beneficial to all stakeholders. Draft part Z, as recommended by the insolvency law committee, is under consideration for enactment,” the ministry said, while proposing the additional measures regarding personal guarantors.
The changes were proposed after the ILC, constituted under the corporate affairs ministry to review the implementation of the IBC, noted the lack of a framework for cross-border insolvency. The government has decided to put in place a comprehensive framework for this purpose based on UNCITRAL model law on cross-border insolvency, which could be made a part of the IBC by inserting a separate chapter for this purpose.
In January 2020, the government had constituted a crossborder insolvency rules/regulations committee to recommend subordinate legislation.
Banks have approached the National Company Law Tribunal for invoking personal guarantees of promoters of 17 defaulting companies.
The defaulting promoters include those of Punj Lloyd, Amtek Auto, ABG Shipyard, Videocon, Varun Shipping, and Lanco, according to reports.
Armed with a Supreme Court order, banks are looking to invoke personal guarantees of tycoons from Venugopal Dhoot to Kapil Wadhawan to recover unpaid loans from their delinquent firms
The guaranteed debt
According to an estimate, the top 10 personal guarantors have guaranteed debt of over Rs 1.6 lakh crore. Among the big names, former promoters of Bhushan Steel and Power Sanjay Singhal and his wife Aarti Singhal had furnished personal guarantees worth up to Rs 24,550 crore to take loans from a consortium of bank led by State Bank of India.
The former promoter of Reliance Communications, Anil Ambani, has also given a personal guarantee against the loan taken. Erstwhile promoter Wadhawan stands guarantee to loans taken by DHFL, which is sitting on debt of about Rs 90,000 crore, while Dhoot has also given a personal guarantee to a portion of Rs 22,000 crore loan to Videocon.
[ad_2]
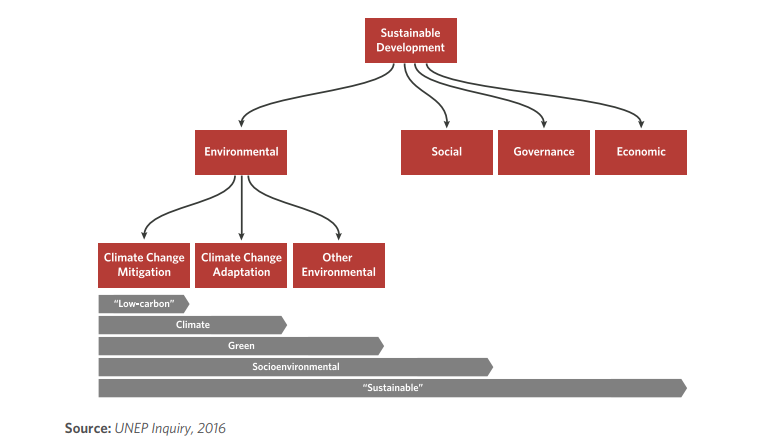
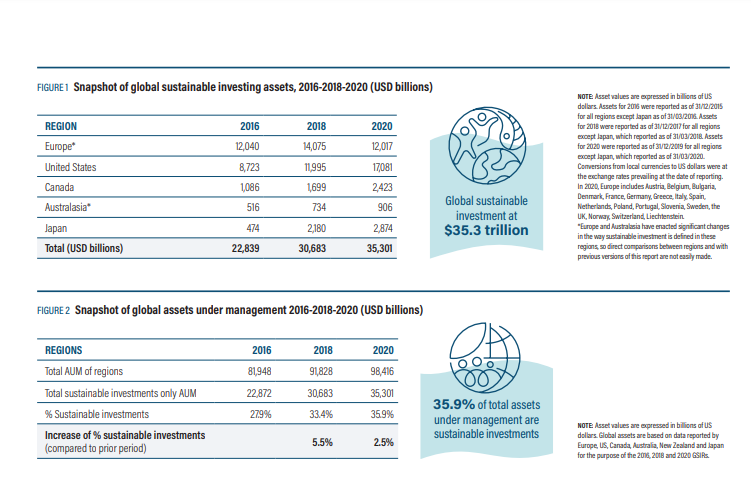 Source: Global Sustainable Investment Alliance
Source: Global Sustainable Investment Alliance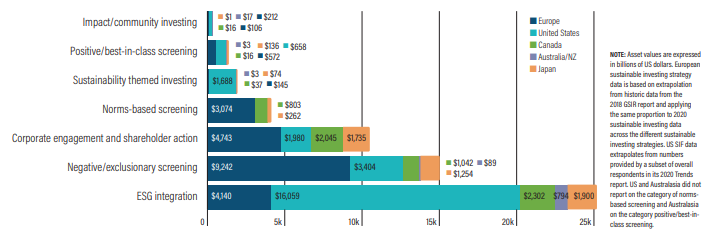 Sustainable investing assets by strategy & region 2020 (Source: Global Sustainable Investment Alliance)
Sustainable investing assets by strategy & region 2020 (Source: Global Sustainable Investment Alliance)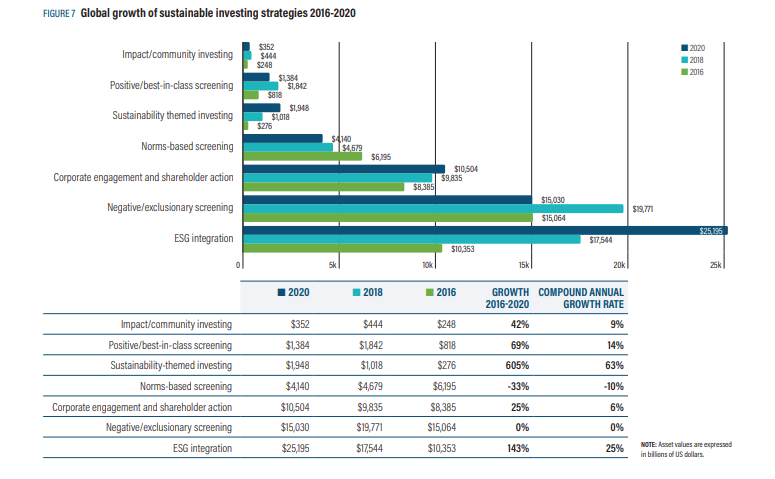 Global growth of sustainable investing strategies 2016-2020 (Source: Global Sustainable Investment Alliance)
Global growth of sustainable investing strategies 2016-2020 (Source: Global Sustainable Investment Alliance)