Decision-day Guide, BFSI News, ET BFSI
[ad_1]
Read More/Less
India’s monetary policy makers are likely to leave interest rates untouched for a seventh straight meeting, as their focus remains more on fixing a fickle economy than on controlling stubborn price pressures.
The Reserve Bank of India’s six-member Monetary Policy Committee is meeting amid weak indicators raising doubts about the economy’s ability to sustain a nascent recovery. Some parts of the nation, where the fast-spreading delta variant was first identified, are still battling a rise in Covid-19 infections with researchers warning of an impending third wave of the pandemic.
All 21 economists surveyed by Bloomberg as of Wednesday afternoon expect the MPC to leave the benchmark repurchase rate unchanged at 4% on Friday. While the RBI is widely expected to announce another tranche of its so-called government securities acquisition program, bond traders will be watching for any cues on return to policy normalization.
For now, Governor Shaktikanta Das has maintained that growth is the main challenge and that inflation, while sticky, is only a “transitory hump.”
Here’s what to watch for in the MPC decision to be announced by Das in Mumbai on Friday morning:
Inflation ‘Chameleon’
The governor is likely to bump up the RBI’s inflation forecasts, given the ripple effect of a sustained rise in input costs along with high fuel taxes.
Headline inflation is already hovering well above the upper tolerance limit of the central bank’s 2%-6% target band, and some economists see the measure breaching the RBI’s 5.1% outlook for this fiscal year to end up in the region of 5.5%, or thereabouts.
“Several inflation drivers have come and gone,” said Pranjul Bhandari, chief India economist at HSBC Holdings Plc. in Mumbai. “But inflation has stayed elevated, like a chameleon, adapting itself rather quickly to the driver of the day. In recent months, price pressures have spread widely across the food and core baskets.”
Growth Prospects
The central bank is likely to retain its growth estimate of 9.5% for the year to March 2022.
A slew of high frequency indicators from purchasing managers’ surveys to mobility indicators and tax collections indicate a rather uneven recovery from the pandemic’s second wave. Hopes that the monsoon rains, which have been below normal in July, will pick up in the August-September period and provide a boost to rural demand is likely to provide some comfort to policy makers who are focused on reviving growth.
Normalization or Not?
With inflation running near the upper end of the RBI’s target and the economy showing signs of a recovery, bond investors are of the view that the central bank could signal when it intends to start unwinding some of its extraordinary easy policy.
Although Das has reiterated that normalization is not on his mind yet, economists are of the view that stubborn inflation could force his hand.
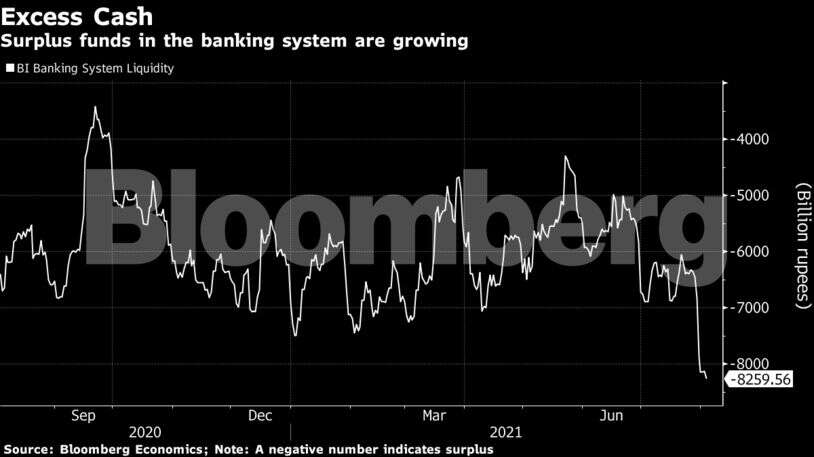
Withdrawing some of the excess funds in the banking system via longer dated reverse repo auctions — an action it took at the start of the calendar year — could be a start of that process. Bloomberg Economics estimates excess cash is at over 8 trillion rupees ($107.8 billion).
“The RBI could re-announce the long tenor variable rate reverse repo auctions as the first step toward normalization,” wrote Samiran Chakraborty, chief India economist at Citigroup Global Markets in Mumbai. “Beyond that, the MPC is unlikely to provide much guidance on the timing and pace of normalization.”
[ad_2]