Indian companies are running out of room to absorb rising raw material costs, which could force the central bank to unwind stimulus faster-than-expected and threaten a stock market rally that has earned billions for investors.
Companies from the Indian unit of Unilever Plc to Tata Motors Ltd., the owner of the iconic Jaguar Land Rover, are increasingly complaining about pricier inputs and are frustrated at not being able to fully pass on costs to consumers reeling from the pandemic-induced economic shock. But it is only a matter of time before the pass- through happens, warn economists.
“Firms are yet to pass on the increase in underlying input costs due to weak demand,” said Sameer Narang, chief economist at Bank of Baroda in Mumbai. “This will change as growth and consumer confidence revives.”
That recovery in consumer optimism may be just around the corner, according to a survey by the Reserve Bank of India. While households were downbeat about the current economic conditions, they are hopeful about the year ahead prospects, the RBI said.
Any increase in prices could end up fanning inflation further and complicating the central bank’s efforts to support the economy. While Governor Shaktikanta Das has so far maintained that the inflation hump is “transitory,” the RBI this month for the first time since October last year saw consensus elude it on the need to keep interest rates lower for longer to ensure a durable economic recovery.
With inflation already hovering above the RBI’s upper tolerance limit of 6% for the past two months, one of the rate setters, Jayanth Rama Varma, expressed “reservations” about continuing with the accommodative policy stance, Das told reporters Friday. The RBI separately raised its inflation forecast for the fiscal year ending March to 5.7% from 5.1% previously, even as Das underlined the effect of higher global commodity prices, broken supply chains and steep local fuel taxes on price-growth.
Data due Thursday will probably show consumer prices rose 5.7% last month, cooling from near 6.3% in June. Wholesale prices — scheduled for release on Monday — are likely to show factory-gate inflation at double digits for a fourth straight month.
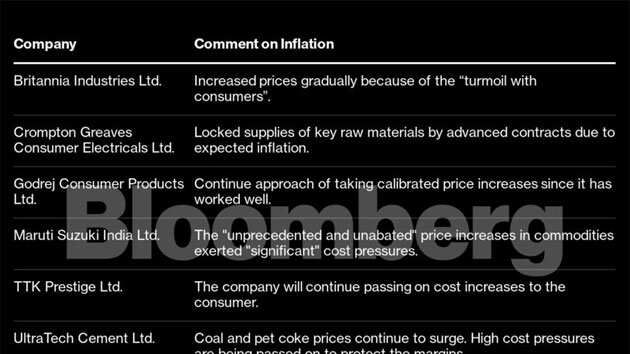
For now, the RBI has kept funding conditions benign, driving a rally in the stock markets. Individual investors by the millions were drawn to stock trading as they chased yields amid inflation and low rates denting returns from traditional sources such as bank deposits. About 14 million first-time electronic trading accounts were opened in the fiscal year ended March 2021, according to India’s market regulator.
For companies too, it’s a fight to protect margins — a crucial ingredient to delivering higher shareholder value. Firms across the manufacturing and services spectrum are grappling with rising input costs for months now, purchasing managers’ surveys show, trying hard to strike a balance between sluggish consumer demand and the need for higher sales and profits.
It is a fight that doesn’t appear to go away in a hurry, especially for manufacturing firms who have had to deal with higher prices of commodities and fuel costs for months on end. For the bulk of the previous financial year, most Indian companies resorted to cost cutting to boost profits, according to a study on corporate performance by the RBI.
“In terms of commodity inflation, I think this is something, which we keep on fighting,” said Girish Wagh, executive director at Tata Motors.
While its a tough balancing act, companies are mindful that something will have to give in eventually. In this case, it could mean higher prices being passed to consumers gradually as a recovery gets stronger in Asia’s third-largest economy.
“If commodity inflation remains, of course, we will have to keep working as we are doing already very hard on our savings agenda, but equally, lead price increases,” said Ritesh Tiwari, chief financial officer at Hindustan Unilever Ltd. These increases will be “required to protect the business model,” he said.
Others aren’t sure if steep price increases are the right way forward. Dabur India Ltd., one of HUL’s competitors, doesn’t favor that route.
“You’re caught between a rock and a hard place,” Dabur’s Chief Executive Officer Mohit Malhotra said, instead opting for calibrated increases. “At one end there is demand, which is not very, very resilient and there is inflation hitting us. So we don’t want to price out ourselves as far as the consumer is concerned.”
While the global debate between whether price pressures are “transitory” or not is still raging, in India, economists are certain that inflation is here to stay. Not surprisingly, bond and swap investors are pricing in chances of a faster-than-expected normalization of monetary policy by the RBI.
“We must differentiate between transitory inflation in developed economies and in India,” said Soumya Kanti Ghosh, chief economic adviser at the State Bank of India.
“Developed economies had not seen inflation at more than 2% even after incessant quantitative easing. In India, inflation is now running close to 6% for the last one year and almost all inflation prints, headline, core, rural and urban are converging at 6% or upwards implying inflation numbers may not be transitory.”
