The months of May, June and July gave a fierce glimpse of the natural disasters – cyclones on east and west coast, excess rainfall, floods and cloudbursts – that reigned havoc in India and are set to increase in frequency and intensity in years to come.
Loss of infrastructure apart from loss of lives and livestock is a major setback after every such disaster. For instance, several areas of Konkan that witnessed huge floods in July were without power for many days as the entire power department infrastructure suffered massive damage. Several metres/kilometres of roads were washed away when the Himalayan states of Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand witnessed landslides and cloudbursts recently.
A crucial report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) on Monday is likely to paint an even dismal scenario with a warning to not just take mitigative steps but also increase adaptation. Therefore, it becomes crucial to understand what is at stake for the financial sector in India. Will India’s finance sector witness an increased understanding of and a push for integrating climate risk in the existing set up of financial institutions?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has been talking about green finance for many years and has taken various steps towards it. It has pushed, on the lines of corporate social responsibility for private companies, the concept of Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) principles into financing aspects. But April 2021 saw an important development vis-a-vis climate finance.
The RBI joined the Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS) in April 2021. The NGFS, launched in December 2017 at the Paris One Planet Summit, is a group of central banks and supervisors from across the globe to share the best practices and contribute to the development of the environment and climate risk management in the financial sector. It is an institutional yet voluntarily membership. It will also help mobilize mainstream finance to support the transition toward a sustainable economy.
The Paris Agreement – that India has signed – has three components. One and the most talked about is the global efforts to restrict the temperature rise to 2 degrees Celsius and if possible, to keep it at 1.5 degrees Celsius. The second is about adaptation to climate impacts. But it is the third that is rarely talked about, i.e. that all finance goals should be aligned with the de-carbonisation or the low carbon pathway.
“It is not yet clear what exactly would be the role of the monetary policy in addressing climate change. We are looking at both, natural disasters which hit infrastructure and also the planning for new infrastructure investments taking into account increased risks. It translates into very simple yet significant decisions, such as ‘how high will you construct a bridge?’ or ‘Where will you locate your airport?'” Director (Climate) at the World Resources Institute (WRI), a think tank, Ulka Kelkar told IANS.
This will mean, choosing the location that will bear the least or minimal impact due to climate change or taking into account that the cost will increase in view of climate proofing the project or there will be a need to have additional insurance, all such things wherein the initial increase in cost can offset the long-term damage, she said.
As per the NGFS literature, its goal is to provide a common framework that will allow central banks, supervisors, and financial firms to assess and manage future climate-related risks. However, it also cautioned that “the use of scenarios by central banks and by companies requires caution”, as they have many limitations that can hamper an accurate assessment of the risks and potentially harm financial decisions and climate risk management practices.
The NGFS has given a very easy way to understand four ‘Climate Scenarios Framework’: ‘Disorderly’ (Sudden and unanticipated response is disruptive but sufficient enough to meet climate goals); ‘Orderly’ (We start reducing emissions now in a measured way to meet climate goals); ‘Too little, too late’ (We do’t do enough to meet climate goals, presence of physical risk spurs a disorderly transition) and ‘Hot house world’ (We continue to increase emissions, doing very little, if anything, to avert the physical risks).
The 22nd Financial Stability Report (FSR22) of the RBI had, about the “climate-related risk” that the value of financial assets/liabilities could be affected either by continuation in climate change (physical risks), or by an adjustment towards a low-carbon economy (transition risks). The manifestation of physical risks could lead to a sharp fall in asset prices and increase in uncertainty, it said.
“A disorderly transition to a low carbon economy could also have a destabilising effect on the financial system. Climate-related risks may also give rise to abrupt increases in risk premia across a wide range of assets amplifying credit, liquidity and counterparty risks,” it said in no uncertain terms.
According to NGFS, there is a growing understanding that climate-related risks should be incorporated into financial institutions’ balance sheets. It said, ‘physical’ risks arise from both ‘chronic’ impacts, such as sea level rise and desertification, and the increasing severity and frequency of ‘acute’ impacts, such as storms and floods. The ‘transition risks’ are associated with structural changes emerging as the economy becomes low and zero-carbon.
RBI’s 23rd Financial Stability Report (FSR23) released last month under its ‘Systemic Risk Survey’ mentioned as ‘declined’ the risk due to ‘climate change’ in the general risk category. Earlier, the FSR22 released in January 2021 had mentioned as ‘increased’ the risk due to ‘climate change’ in the general risk category.
In the FSR21 released in July 2020, the climate change related risk had ‘decreased’; in the FSR20 released in December 2019, it had ‘decreased’; in the FSR19 released in June 2019, it had ‘increased’ while it had remained ‘decreased’ both in FSR18 (December 2018) and FSR17 (June 2018).
Explained a financial sector analyst, who did not wish to be named, “This is a quarterly survey where the RBI asks respondents about their views on various kinds of risks with regard to financial stability. The view about risks may change from quarter to quarter depending on the emerging and anticipated scenario. For the lay person, the risk analysis is done on the basis of the respondents’ perception about certain scenarios.”
However, specific queries via mail and text messages to the RBI Chief General Manager, Corporate Communications Yogesh Dayal, about what changes the risk perception in the ‘ystemic Risk Survey’ and has the RBI’s joining NGFS changed the risk perception vis-à-vis climate change, remained unanswered.
Earlier, the FSR19 had mentioned that how a report from the International Association of Insurance Supervisors (IAIS) posits that non-incorporation of physical risks arising due to climate change can potentially result in under-pricing/under reserving, thereby overstating insurance sector resilience.
As per RBI documents available in public domain, a key prerequisite to climate risk assessment exercise for India is to develop emission reduction pathways for energy intensive sectors and “map them onto macroeconomic and financial variables and integrate them with quantitative climate risk related disclosures to develop a holistic approach to addressing the financial stability risks arising out of climate change.”
The ‘cross industry, cross disciplinary’ forum as mentioned by the RBI is the need of the hour.
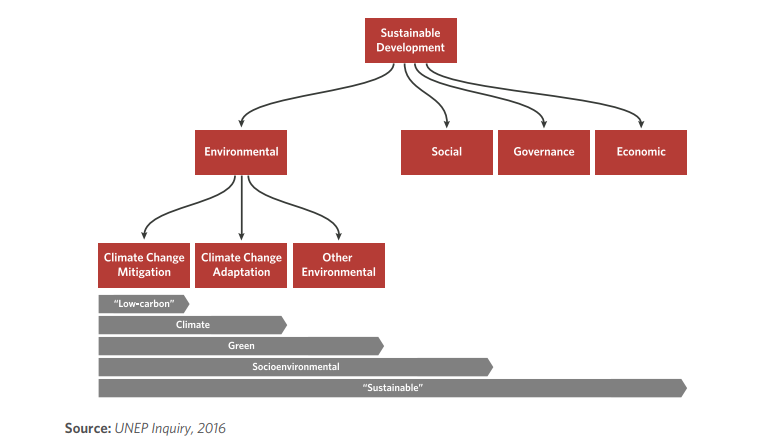
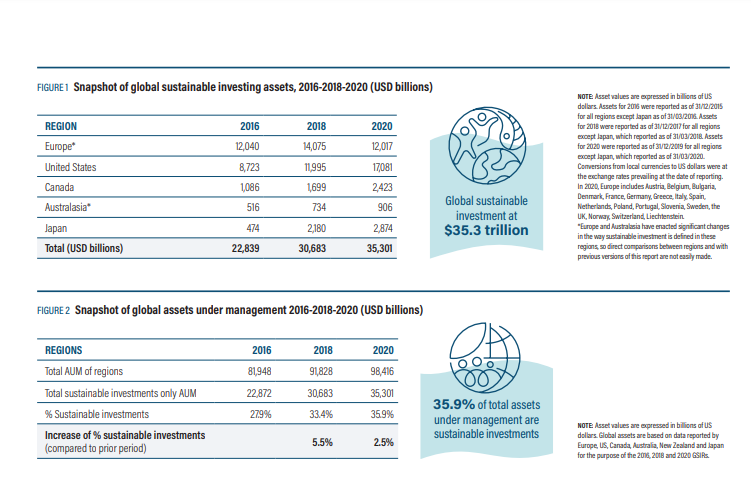 Source: Global Sustainable Investment Alliance
Source: Global Sustainable Investment Alliance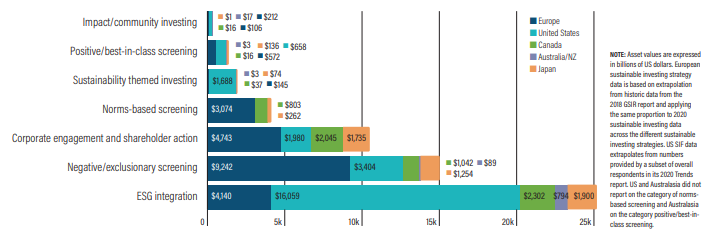 Sustainable investing assets by strategy & region 2020 (Source: Global Sustainable Investment Alliance)
Sustainable investing assets by strategy & region 2020 (Source: Global Sustainable Investment Alliance)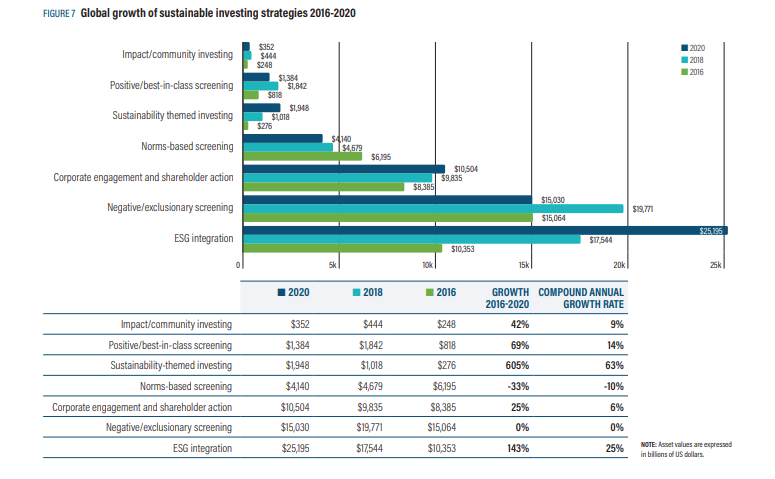 Global growth of sustainable investing strategies 2016-2020 (Source: Global Sustainable Investment Alliance)
Global growth of sustainable investing strategies 2016-2020 (Source: Global Sustainable Investment Alliance)