India’s risk-averse lenders are emerging as one of the biggest hurdles to the speed of the nation’s recovery from the pandemic-induced downturn, as they hold back credit when the economy needs it the most.
Loans to companies and individuals has been growing at a subdued 5.5%-6% in recent months, which is half the pace seen before the pandemic struck, Reserve Bank of India data shows. The nation’s biggest lender State Bank of India wants to nearly double its credit growth rate to 10% in the year started April 1, but is willing to miss the goal.
“It is a very fragile situation,” Dinesh Khara, chairman of SBI, said after reporting earnings for the fiscal year ended March. The bank would not “compromise” on asset quality to achieve targets, he said.
Khara’s comments underline the biggest obstacle to both credit off-take and economic growth, pegged at 9.5% this year, already reduced from the central bank’s previous forecast of 10.5% and following an unprecedented contraction last year. Banks’ risk aversion — or the fear of soured loans jumping in a tough economic environment — could slow the economy’s recovery further, according to analysts, including those at the RBI.
“Credit is a necessary and probably most important ingredient for economic growth,” according to S. S. Mundra, a former deputy governor of RBI, who estimated that the multiplier effect of credit on nominal gross domestic product growth is 1.6 times.
It doesn’t help India’s case that it’s already home to one of the biggest piles of soured loans among major economies. And add to that a crisis in the shadow banking sector, which culminated in the rescue of two lenders and bankruptcy of two more over the past couple of years.
The RBI expects banks’ bad-loan ratio to rise to 9.8% by the end of this financial year from 7.48% a year ago.
Sluggish Capex
While banks are dithering on loans on the one hand, companies are pushing back investment plans amid lack of demand on the other.
Corporate willingness for new investments is low, according to the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy Pvt., with capital expenditure declining. While companies have posted bumper profits mostly on the back of widespread cost cutting, most have used the extra funds generated to pay down bank loans.
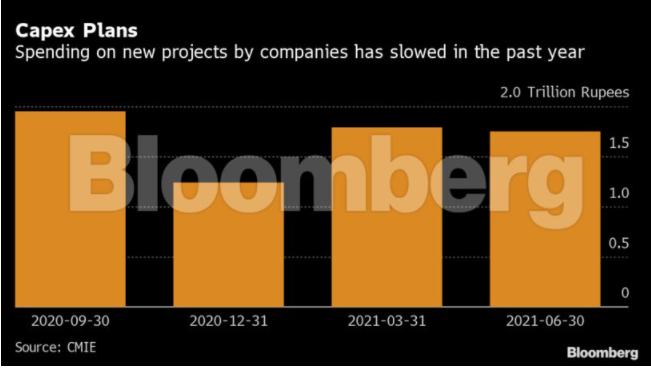
According to research from SBI, where economists analyzed the top 15 sectors and a thousand listed companies, more than 1.7 trillion rupees ($22.8 billion) worth of debt was pared last year. Refineries, steel, fertilizers, mining and mineral products as well as textile companies alone reduced debt by more than 1.5 trillion rupees, with the trend continuing this year, the bank’s chief economist Soumya Kanti Ghosh wrote recently.
“Any meaningful recovery beyond a 10% growth in credit demand will require a substantial turn in the private capex cycle, which still seems sometime away as corporates are focused on deleveraging,” said Teresa John, economist at Nirmal Bang Equities Pvt. in Mumbai. She forecasts GDP growth of 7% this year, which is at the lower end of a Bloomberg survey with consensus at 9.2%.
What Bloomberg Economics Says…
“A further slump in credit growth means that the RBI is likely to allow some more time for credit recovery to take shape before its begins to unwind its stimulus measures.”
— Abhishek Gupta, India economist
Consumers too are repairing their finances, which bodes ill for overall demand for goods and services as well as retail loans, and in turn economic growth. The current recovery is likely to be less steep than the bounce that unfolded in late 2020 and early 2021, according to analysts at S&P Global Ratings.
“Households are running down savings,” the S&P analysts wrote. “A desire to rebuild their cash holding may delay spending even as the economy reopens.”
And while Covid-19 relief measures may provide banks some reprieve, the need to raise capital will remain high once virus related stress start to emerge on their balance sheets.
“Indian banks’ challenges posed by the coronavirus pandemic have increased due to a virulent second wave,” Fitch Ratings’ Saswata Guha and Prakash Pandey said this week, as they cut India’s growth forecast by 280 basis points to 10%. That underlines “our belief that renewed restrictions have slowed recovery efforts and left banks with a moderately worse outlook for business and revenue generation.”




